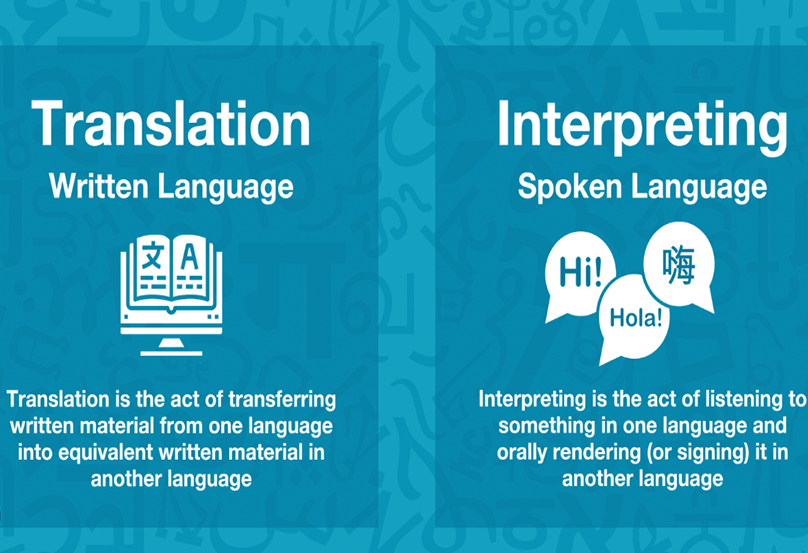
Translation and interpretation work involves converting written text or spoken language from one language to another. Both processes require linguistic skills and cultural understanding to ensure accurate and effective communication between different language speakers. Here’s a step-by-step guide to the right process of translation and interpretation work:
1. Understand the Project Requirements:
Before starting any translation or interpretation work, thoroughly understand the project requirements. Determine the target languages involved, the subject matter, the purpose of the translation or interpretation, and any specific instructions or guidelines.
2. Select Qualified Linguists:
Choose qualified and experienced linguists for the translation or interpretation task. Linguists should be fluent in both the source and target languages and have a deep understanding of the subject matter and cultural nuances.
3. Gather Reference Material:
For translation projects, provide the linguists with reference materials, such as glossaries, style guides, previous translations, and any relevant context to ensure consistency and accuracy.
4. Prepare for Interpretation:
For interpretation assignments, familiarize interpreters with the event or meeting agenda, important terminologies, and any specific instructions or protocols.
5. Translate or Interpret the Content:
The linguists will begin the translation or interpretation process based on the provided materials and project requirements. They will strive to maintain the intended meaning, tone, and context of the original message.
6. Review and Editing:
After completing the translation or interpretation, perform a thorough review and editing process to ensure accuracy, clarity, and adherence to project guidelines. This step helps eliminate errors and improve the quality of the final output.
7. Cultural Adaptation:
In both translation and interpretation, linguists must consider cultural differences and adapt the content to be culturally appropriate for the target audience.
8. Proofreading:
Perform a final proofreading check to catch any remaining errors or inconsistencies. This step is critical to deliver a polished and professional result.
9. Feedback and Collaboration:
Collaborate with the client or end-users to gather feedback on the translation or interpretation. Address any concerns or questions to ensure the final product meets their needs.
10. Delivery and Formatting:
Provide the final translated text or interpretation to the client in the required format, whether it’s a written document, subtitles, an audio recording, or a live interpretation service.
11. Confidentiality and Data Security:
Maintain confidentiality and ensure data security throughout the translation and interpretation process, especially when dealing with sensitive information.
12. Continuous Improvement:
Encourage continuous improvement by seeking feedback from clients, linguists, and end-users. This feedback can help identify areas for improvement and enhance the overall quality of future translation and interpretation work.
Remember that translation and interpretation work require linguistic expertise, cultural sensitivity, and a commitment to accuracy. Following a systematic and well-defined process ensures that the final output meets the highest standards and effectively bridges language and cultural barriers.